Construction Site Generator Sizing
Construction tools utilize electric motors which have special startup power requirements. When a motor starts, it uses up to six times the rated power for one and a half to three seconds. A generator starting that motor must be capable of supplying the motor’s inrush current during startup. If multiple tools will operate from the generator at the same time, consider the starting current of each motor.
Power tool motors fall into two categories: the universal motor and the capacitor start motor. Universal motors power easy to start tools such as electric drills, circular saws, disc grinders and jig saws. The number of starting watts for each tool is approximately double the number of run watts. Each tool has a nameplate marked with the voltage and the amps and should also include the LR or LRA. Multiply amps by volts for watts, then double the number of watts to determine starting watts.
 Tools that use capacitor start motors are shown on the nameplate as type G or type L motors. These include table saws, brick or metal cut-off saws, air compressors, and pumps. Running watts are determined by multiplying volts by amps as shown on the tool nameplate. Type G motors require three times the running watts to start; type L motors need six times the running watts at startup.
Tools that use capacitor start motors are shown on the nameplate as type G or type L motors. These include table saws, brick or metal cut-off saws, air compressors, and pumps. Running watts are determined by multiplying volts by amps as shown on the tool nameplate. Type G motors require three times the running watts to start; type L motors need six times the running watts at startup.
Example: An air compressor with a type G motor draws 10 amps at 120 volts or 1200 watts. 1200 watts x 3 = 3600 watts.
Example: A circular saw runs a universal motor at 12.5 amps. 120 volts x 12.5 amps = 1500 watts. The starting watts is 1500 x 2 = 3000 watts.
If multiple tools will operate at the same time, total up the running watts for all the tools, then add the highest starting watts to the total running watts.
Example: A construction site has two workers using circular saws and a 1 horsepower air compressor. The compressor runs at 1200 watts, but needs 3600 watts to start. The two saws run at 1500 watts and need 3000 watts each to start.
Running Watts Required: 1500 + 1500 + 1200 = 4200 Running Watts.
Starting Watts Required: 4200 + 3600 = 7800 Watts.
The minimum generator capacity for this job site is 4200 running watts and 7800 Starting watts. However, when all three motors are running, the generator is working at maximum capacity. Add a 25 percent margin and the generator won't work quite so hard.
4200 Watts + 1050 Watts (25% margin) = 5250 Watts
Pick a generator with 7800-8000 Starting Watts and at least 5200 Running Watts. That way, the generator doesn't run at maximum capacity which will extend its life.
One important feature on a contractor generator is a low idle. With low idle, anytime the power use falls to zero, the generator engine slows down to use less fuel, reduce wear and tear, and as a bonus, make less noise.
Need more information? Pick The Best Portable Generator for Contractors and Job Sites
Sizing Generators for Recreational or Emergency Use
The loads supplied by a portable generator for recreational use are either resistive loads or motor loads. Small motors for window fans, grill rotisseries, decorative lights and lighting are all considered resistive loads for the purpose of sizing a portable generator. Each device is marked on a nameplate with its power requirements, or the information is supplied in the owners manual or user guide.
Larger motors such as refrigerators, freezers and air conditioners require about three times the starting watts of the motor.
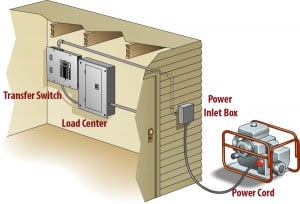
Hardwired appliances like a furnace, well pump, or central air conditioner can't plug into a generator outlet. To use these appliances, a Manual Transfer Switch for a Portable Generator powers your hardwired circuits. A single Generator Cord between the generator and the house plugs into an inlet box, eliminating or reducing the number of extension cords required.
Example: A 5000 BTU window air conditioner uses about 600 watts, but needs 600 watts x 3 = 1800 watts of power each time the unit’s compressor starts.
Total the power requirements for each device the generator will supply, including the starting watts for larger motors, and the sum indicates the generator size required.
Pick the Best Portable Generator for Camping and Tailgating
*Note: Generator Sizing Guides are for estimating purposes only. Actual power requirements of high demand appliances vary widely by brand, model and capacity. Always have an authorized dealer or qualified electrician analyze your specific requirements before making a purchase decision.
Read Next |> Planning a Manual Transfer Switch Installation (1/4)